By InfiniEnergy | 27 May 2017 | 0 Bemerkungen
What is Lithium Battery?
Lithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery (abbreviated as LIB) is a type of rechargeable battery in which lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge and back when charging. Li-ion batteries use an intercalated lithium compound as one electrode material, compared to the metallic lithium used in a non-rechargeable lithium battery. The electrolyte, which allows for ionic movement, and the two electrodes are the constituent components of a lithium-ion battery cell.
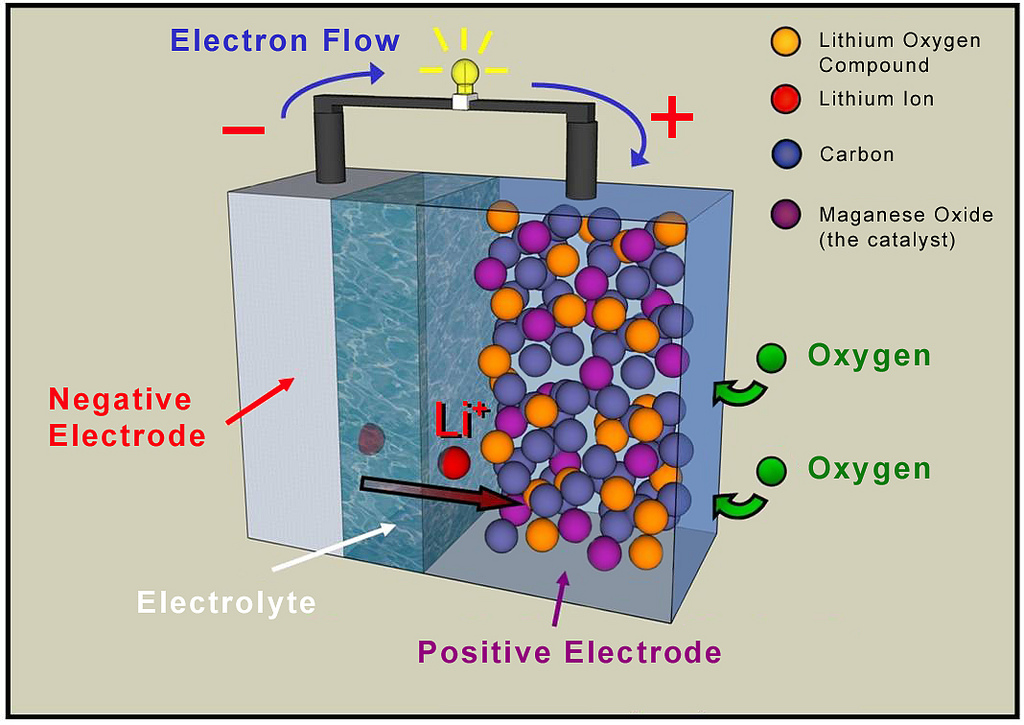
Anode, cathode, electrode
In electrochemistry, the anode is the electrode where oxidation is taking place in the battery, i.e. electrons get free and flow out of the battery (technical current flowing into it). However, this happens on opposite electrodes during charge vs. discharge. The less ambiguous terms are positive (cathode on discharge) and negative (anode on discharge). This is the positive-negative polarity which is displayed on a volt meter.[20] For rechargeable cells, the term "cathode" designates the positive electrode in the discharge cycle, even when the associated electrochemical reactions change their places when charging and discharging, respectively. For lithium-ion cells the positive electrode ("cathode") is the lithium based one.
Chemistry category
Chemistry, performance, cost and safety characteristics vary across LIB types. Handheld electronics mostly use LIBs based on lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), which offers high energy density, but presents safety risks, especially when damaged. Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium ion manganese oxide battery (LiMn2O4, Li2MnO3, or LMO) and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (LiNiMnCoO2 or NMC) offer lower energy density, but longer lives and inherent safety. Such batteries are widely used for electric tools, medical equipment and other roles. NMC in particular is a leading contender for automotive applications. Lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (LiNiCoAlO2 or NCA) and lithium titanate (Li4Ti5O12 or LTO) are specialty designs aimed at particular niche roles. The newer lithium–sulfur batteries promise the highest performance-to-weight ratio.
Shapes
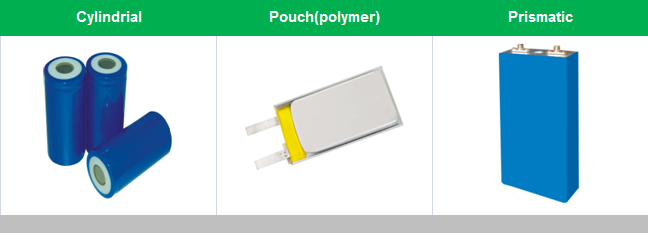
Li-ion cells (as distinct from entire batteries) are available in various shapes, which can generally be divided into four groups:
Small cylindrical (solid body without terminals, such as those used in laptop batteries)
Large cylindrical (solid body with large threaded terminals)
Pouch (soft, flat body, such as those used in cell phones; also referred to as li-ion polymer or lithium polymer batteries)
Prismatic (semi-hard plastic case with large threaded terminals, such as vehicles' traction packs)
Charge and discharge
During discharge, lithium ions (Li+) carry the current within the battery from the negative to the positive electrode, through the non-aqueous electrolyte and separator diaphragm.
During charging, an external electrical power source (the charging circuit) applies an over-voltage (a higher voltage than the battery produces, of the same polarity), forcing a charging current to flow within the battery from the positive to the negative electrode, i.e. in the reverse direction of a discharge current under normal conditions. The lithium ions then migrate from the positive to the negative electrode, where they become embedded in the porous electrode material in a process known as intercalation.
Self-discharge
Batteries gradually self-discharge even if not connected and delivering current. Li+ rechargeable batteries have a self-discharge rate typically stated by manufacturers to be 1.5-2% per month.The rate increases with temperature and state of charge. A 2004 study found that for most cycling conditions self-discharge was primarily time-dependent; however, after several months of stand on open circuit or float charge, state-of-charge dependent losses became significant. The self-discharge rate did not increase monotonically with state-of-charge, but dropped somewhat at intermediate states of charge.Self-discharge rates may increase as batteries age.
For comparison, the self-discharge rate is over 30% per month for common nickel metal hydride (NiMH) batteries,dropping to about 1.25% per month for low self-discharge NiMH batteries, and 10% per month in nickel-cadmium batteries.
Battery life
Rechargeable battery life is typically defined as the number of full charge-discharge cycles before significant capacity loss. Inactive storage may also reduce capacity.
Manufacturers' information typically specify lifespan in terms of the number of cycles (e.g., capacity dropping linearly to 80% over 500 cycles), with no mention of chronological age. On average, lifetimes consist of 1000 cycles, although battery performance is rarely specified for more than 500 cycles. This means that batteries of mobile phones, or other hand-held devices in daily use, are not expected to last longer than three years. Some batteries based on carbon anodes offer more than 10,000 cycles.
As a battery discharges, its voltage gradually diminishes. When depleted below the protection circuit's low-voltage threshold (2.4 to 2.9 V/cell, depending on chemistry) the circuit disconnects and stops discharging until recharged. As discharge progresses, metallic cell contents plate onto its internal structure, creating an unwanted discharge path.
Defining battery life via full discharge cycles, is the industry standard, but may be biased, since full depth of discharge (DoD)/recharge may itself diminish battery life, compared to cumulative Ah partial discharge/charge performance. Projection from the standard to specific use patterns may require additional factors, e.g. DoD, rate of discharge, temperature, etc.
Uses
Li-ion batteries provide lightweight, high energy density power sources for a variety of devices. To power larger devices, such as electric cars, connecting many small batteries in a parallel circuit is more effective and more efficient than connecting a single large battery.Such devices include:
Portable devices: these include mobile phones and smartphones, laptops and tablets, digital cameras and camcorders, electronic cigarettes, handheld game consoles and torches (flashlights).
Power tools: Li-ion batteries are used in tools such as cordless drills, sanders, saws and a variety of garden equipment including whipper-snippers and hedge trimmers.
Electric vehicles: Because of their light weight Li-ion batteries are used for propelling a wide range of electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles, such as aircraft,electric cars, Pedelecs, advanced electric wheelchairs, radio-controlled models, model aircraft and the Mars Curiosity rover.
Hinterlasse eine Antwort
Ihre E-Mail-Adresse wird nicht veröffentlicht. Erforderliche Felder sind markiert. *
BELIEBTER BLOG
KATEGORIEN
STICHWORTE